Rasabox︎︎︎
Rasabox is a movement technique developed by
the theater director and scholar Richard Schechner, which focuses on exploring
the relationship between emotions, physical sensations, and movement.
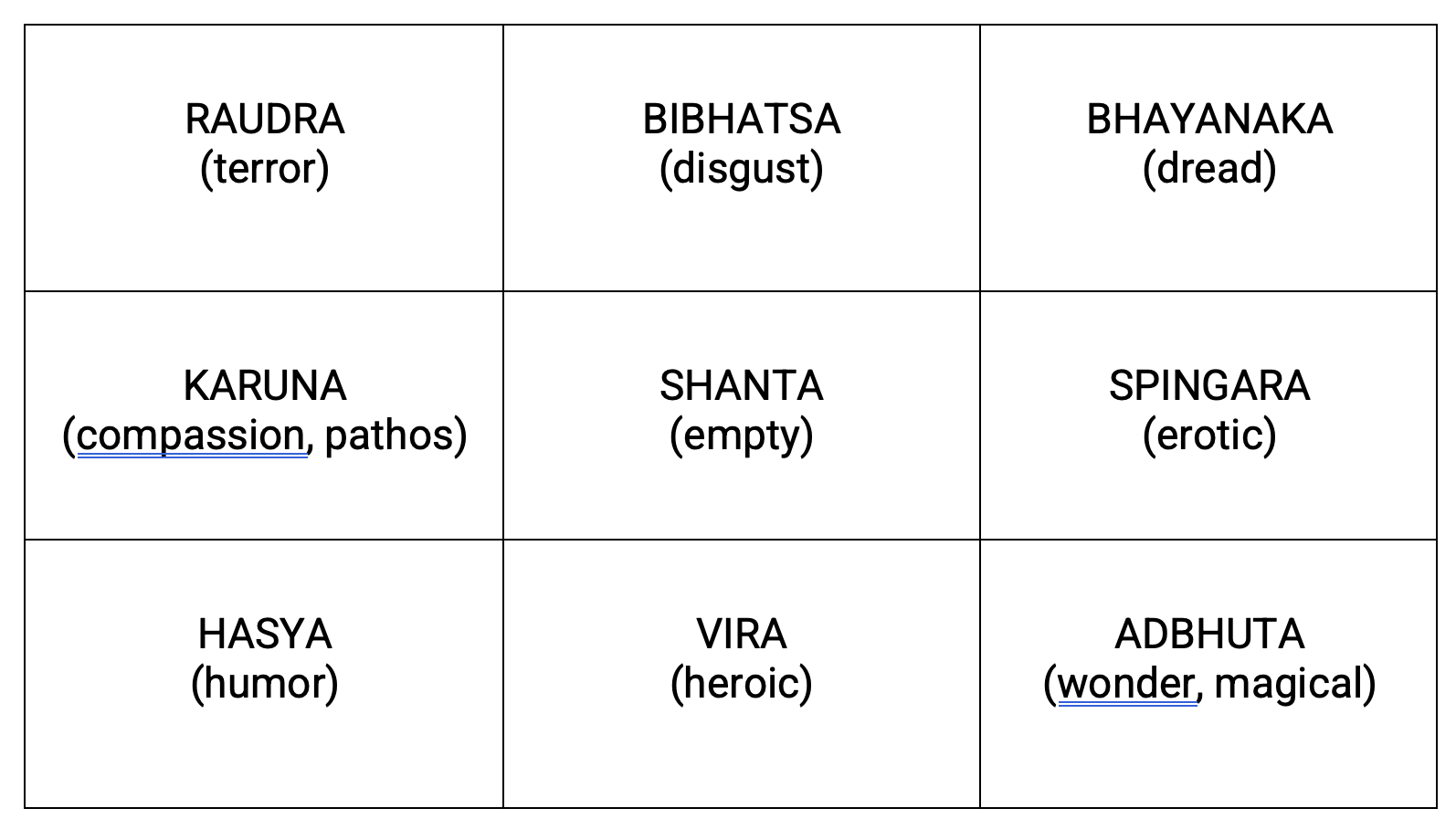
The name "Rasabox" comes from the Sanskrit word "rasa," which means "emotion," and "box," which refers to the nine emotional states that the technique explores. These states are:
![]()
A typical Rasabox exercise involves nine performers arranged in a square or circle, with each performer representing one of the nine emotional states. The performers may be standing, sitting, or moving around within their designated space. As the exercise progresses, each performer takes turns expressing their emotion through movement and vocalization, while the other performers observe and respond.
The movements and vocalizations associated with each emotion are typically stylized and exaggerated, and may involve gestures, facial expressions, and vocal sounds that reflect the particular emotional state. The performers may also interact with each other, either through mirroring, responding, or contrasting each other's movements and sounds.
The name "Rasabox" comes from the Sanskrit word "rasa," which means "emotion," and "box," which refers to the nine emotional states that the technique explores. These states are:
- Shanta (peace)
- Raudra (anger)
- Hasya (laughter)
- Karuna (compassion)
- Veera (courage)
- Bhayanaka (fear)
- Adbhuta (wonder)
- Bibhatsa (disgust)
- Shringara (love)
A typical Rasabox exercise involves nine performers arranged in a square or circle, with each performer representing one of the nine emotional states. The performers may be standing, sitting, or moving around within their designated space. As the exercise progresses, each performer takes turns expressing their emotion through movement and vocalization, while the other performers observe and respond.
The movements and vocalizations associated with each emotion are typically stylized and exaggerated, and may involve gestures, facial expressions, and vocal sounds that reflect the particular emotional state. The performers may also interact with each other, either through mirroring, responding, or contrasting each other's movements and sounds.






